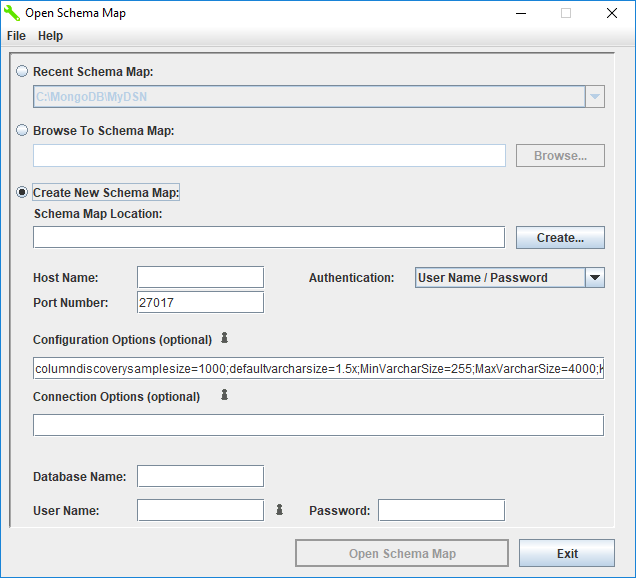
|
Option
|
Characteristic
|
|
Host Name
|
Specifies the name or the IP address of the server to which you want to connect.
|
|
Port Number
|
Specifies the port number of the server listener.
|
|
Config Option
|
Characteristic
|
|
columnDiscoverySampleSize
|
Specifies the number of rows the driver fetches per collection when sampling data to detect columns and gather column statistics. The information collected in these samples is used when defining a schema definition with the Schema Tool. Larger fetch sizes return samples that are more representative of your data, but at the expense of slower performance when generating a configuration file. See About Column Information and Statistics for additional information on how sampling is used for statistics.
The default is 1000.
|
|
DefaultVarcharSize
|
Determines the default length of fields that are mapped as VARCHAR.
Valid values:
length | multiplier
where:
length
is the default length in characters given to columns that are discovered and mapped as VARCHAR.
multiplier
is a positive number immediately followed by the character x. For example, 3x. The positive integer is multiplied by the size of the largest object detected in a column to determine the default VARCHAR length for that column.
Note: When specifying a multiplier, you can define the maximum and minimum limits of the default length generated with the MaxVarcharSize and MinVarcharSize config options.
The default is 1.5x
|
|
KeywordConflictSuffix
|
Specifies a string of up to five alphanumeric characters that the driver appends to any object or field name that conflicts with a SQL engine keyword.
string
where:
string
is a string of up to five alphanumeric characters.
For example, a field called CASE exists in the native MongoDB data. To avoid a naming conflict with the SQL engine keyword CASE, you could set KeywordConflictSuffix=TAB. In this scenario, the driver maps the Case object to the CASETAB column.
There is no default value.
|
|
LeadingUnderscoreReplacement
|
LeadingUnderscoreReplacement specifies the string of characters that replace leading underscores used in identifiers for collections, documents, and arrays.
Valid values:
string
where:
string
is comprised of any Unicode character or group of characters, including spaces.
For example, MongoDB collections automatically include the _id field. By specifying LeadingUnderscoreReplacement=XX, the _id field becomes the XXID column in the relational view of the data.
Note: The Table Wizard builds table and column identifiers by concatenating the names of nested collections, documents, and arrays. When specifying a value for LeadingUnderscoreReplacement, consider that the total length of identifiers must not exceed 128 characters in length.
There is no default value. When no value is specified, a leading underscore is used in identifiers.
|
|
MaxVarcharSize
|
Specifies the maximum default length of fields that are mapped as VARCHAR when a multiplier is specified for the DefaultVarcharSize config option (DefaultVarcharSize=multiplier).
The default is 4000.
|
|
MinVarcharSize
|
Specifies the minimum default length, in characters, of fields that are mapped as VARCHAR when a multiplier value is specified for the DefaultVarcharSize config option (DefaultVarcharSize=multiplier).
The default is 255.
|
|
SchemaFilter
|
Specifies a comma-separated list of database and collection pairs for which you want the driver to fetch metadata. SchemaFilter can significantly improve connection times by limiting the collections for which metadata is fetched to only those that are required by your application. This value takes the following form:
SchemaFilter=database_name:collection_name[[,database_name:collection_name]...]
See "SchemaFilter (Config Option)" for detailed list of supported values.
|
|
UppercaseIdentifiers
|
Defines how the driver maps identifiers.
If set to true, the driver maps identifiers to uppercase.
If set to false, The driver maps identifiers to the mixed case name of the object being mapped. If mixed case identifiers are used, SQL statements must enclose those identifiers in double quotes, and the case of the identifier, must exactly match the case of the identifier name.
See "Naming Conflicts" for additional information about using identifiers.
The default is true.
Note: If you receive an error message indicating that naming conflicts have occurred, you must specify the UppercaseIdentifiers config options to false before the driver will connect to a database.
|
|
Connection Option Attribute
|
Valid Values
|
|
EncryptionMethod
|
The method used to encrypt data sent between the Schema Tool and the database server. If set to noEncryption, data is not encrypted.
If set to SSL, data is encrypted using SSL. If the server is not configured for SSL, the connection fails.
Note: The driver and Schema Tool use different valid values for the EncryptionMethod option.
|
|
HostNameInCertificate
|
A host name for certificate validation when SSL encryption is enabled (Encryption Method=SSL) and validation is enabled (Validate Server Certificate=true).
|
|
KeyPassword
|
The password used to access the individual keys in the keystore file when SSL is enabled (Encryption Method=SSL) and SSL client authentication is enabled on the database server.
|
|
Keystore
|
The fully qualified path and file name of the keystore file to be used when SSL is enabled (Encryption Method=SSL) and SSL client authentication is enabled on the database server.
|
|
KeystorePassword
|
The password used to access the keystore file when SSL is enabled (Encryption Method=SSL) and SSL client authentication is enabled on the database server.
|
|
Truststore
|
The fully qualified path and file name for the truststore file to be used when SSL is enabled (Encryption Method=SSL) and server authentication is used. The password that is used to access the truststore file when SSL is enabled (
|
|
TruststorePassword
|
Encryption Method=SSL) and server authentication is used.
|
|
LoginID
|
The default user ID that is used to connect to your database. Your ODBC application may override this value or you may override it in the logon dialog box or connection string.
|
|
ValidateServerCertificate
|
Determines whether the Schema Tool validates the certificate that is sent by the database server when SSL encryption is enabled.
If set to true, the driver validates the certificate that is sent by the database server. Any certificate from the server must be issued by a trusted CA in the truststore file. If the Host Name In Certificate option is specified, the driver also validates the certificate using a host name. The Host Name In Certificate option provides additional security against man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks by ensuring that the server the driver is connecting to is the server that was requested.
If set to false, the driver does not validate the certificate that is sent by the database server. The driver ignores any truststore information specified by the Trust Store and Trust Store Password options.
Note: The driver and Schema Tool use different valid values for the ValidateServerCertificate option.
|
|
Option
|
Characteristic
|
|
Database Name
|
Specifies the name of the database to which you want to connect.
|
|
User Name
|
If Use Authentication is selected, specifies the user ID that is used to connect to your database.
|
|
Password
|
If Use Authentication is selected, specifies the password to use to connect to your database.
|