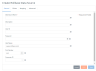
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
Data Source Name
|
A unique name for the data source. Data source names can contain only alphanumeric characters, underscores, and dashes.
|
|
Description
|
A description of this set of connection parameters.
|
|
User Id, Password
|
Login credentials for a Rollbase Private Cloud account with sufficient permissions to access the data of interest.
By default, the characters in the Password field you type are not shown. If you want the password to be displayed in clear text, click the eye
 icon. Click the icon again to conceal the password. icon. Click the icon again to conceal the password.
|
|
Host Name
|
The name of the host on which Rollbase is installed. In a multi-server environment, the host on which you installed the Master server. You can confirm the hostname by navigating to Setup > Application Setup > SOAP API > URI. The host name is the part of the URL following http:// and preceding the port number. For example, in the following URL, mercury is the host name: http://mercury:8080/webapi/services/rpcrouter.
|
|
Port Number
|
The port number to access Rollbase Private Cloud. The default is 443, which is the port used for SSL.
|
|
Connector ID
|
The unique identifier of the On-Premise Connector that is to be used to access the on-premise data source. Select the Connector that you want to use from the dropdown. The identifier can be a descriptive name, the name of the machine where the Connector is installed, or the Connector ID for the Connector.
If you have not installed an On-Premise Connector, and no Connectors have been shared with you, this field and drop-down list are empty.
If you own multiple Connectors that have the same name, for example, Production, an identifier is appended to each Connector, for example, Production_dup0 and Production_dup1. If the Connectors in the dropdown were shared with you, the owner's name is appended, for example, Production(owner1) and Production(owner2).
|
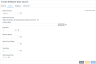
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
OData Version
|
Enables you to choose from the supported OData versions. OData configuration made with one OData version will not work if you switch to a different OData version. If you want to maintain the data source with different OData versions, you must create different data sources for each of them.
|
|
OData Access URI
|
Specifies the base URI for the OData feed to access your data source, for example, https://hybridpipe.operations.com/api/odata/<DataSourceName>. You can copy the URI and paste it into your application's OData configuration.
The URI contains the case-insensitive name of the data source to connect to, and the query that you want to execute. This URI is the OData Service Root URI for the OData feed. The Service Document for the data source is returned by issuing a GET request to the data source's service root.
The OData Service Document returns the names of the entities exposed by the Data Source OData service. To get details such as the properties of the entities exposed, the data types for those properties and the relationships between entities, the Service Metadata Document can be fetched by adding /$metadata to the service root URI.
|
|
Schema Map
|
Enables OData support. If a schema map is not defined, the OData API cannot be used to access the data store using this data source definition. Use the Configure Schema editor to select the tables/columns to expose through OData.
See Configuring data sources for OData connectivity and working with data source groups for more information.
|
|
Page Size
|
Determines the number of entities returned on each page for paging controlled on the server side. On the client side, requests can use the $top and $skip parameters to control paging. In most cases, server side paging works well for large data sets. Client side pagination works best with a smaller data sets where it is not as expensive to fetch subsequent pages.
Valid Values: 0 | n
where n is an integer from 1 to 10000.
When set to 0, the server default of 2000 is used.
Default: 0
|
|
Refresh Result
|
Controls what happens when you fetch the first page of a cached result when using Client Side Paging. Skip must be omitted or set to 0. You can use the cached copy of that first page, or you can re-execute the query to get a new result, discarding the previously cached result. Re-executing the query is useful when the data being fetched may change between two requests for the first page. Using the cached result is useful if you are paging back and forth through results that are not expected to change.
Valid Values:
When set to 0, the OData service caches the first page of results.
When set to 1, the OData service re-executes the query.
Default: 1
|
|
Inline Count Mode
|
Specifies how the connectivity service satisfies requests that include the $count parameter when it is set to true (for OData version 4) or the $inlinecount parameter when it is set to allpages (for OData version 2). These requests require the connectivity service to include the total number of entities that are defined by the OData query request. The count must be included in the first page in server-driven paging and must be included in every page when using client-driven paging.
The optimal setting depends on the data store and the size of results. The OData service can run a separate query using the count(*) aggregate to get the count, before running the query used to generate the entities. In very large results, this approach can often lead to the first page being returned faster. Alternatively, the OData service can fetch the entire result before returning the first page. This approach works well for small results and for data stores that cannot optimize the count(*) aggregate; however, it may have a longer initial response time for the first page if the result is large.
Valid Values:
When set to 1, the connectivity service runs a separate count(*) aggregate query to get the count of entities before executing the query to return results. In very large results, this approach can often lead to the first page being returned faster.
When set to 2, the connectivity service fetches all entities before returning the first page. For small results, this approach is always faster. However, the initial response time for the first page may be longer if the result is large.
Default: 1
|
|
Top Mode
|
Indicates how requests typically use $top and $skip for client side pagination, allowing the service to better anticipate how to process queries.
Valid Values:
Set to 0 when the application generally uses $top to limit the size of the result and rarely attempts to get additional entities by combining $top and $skip.
Set to 1 when the application uses $top as part of client-driven paging and generally combines $top and $skip to page through the result.
Default: 0
|
|
OData Read Only
|
Controls whether write operations can be performed on the OData service. Write operations generate a 405 Method Not Allowed response if this option is enabled.
Valid Values:
ON | OFF
When ON is selected, OData access is restricted to read-only mode.
When OFF is selected, write operations can be performed on the OData service.
Default: OFF
|
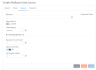
|
Field
|
Description
|
||||||||
|
Map Name
|
Optional name of the map definition that the Hybrid Data Pipeline connectivity service uses to interpret the schema of the data store. The Hybrid Data Pipeline service automatically creates a name for the map.
If you want to name the map yourself, enter a unique name.
|
||||||||
|
Refresh Schema
|
Controls what happens when you fetch the first page of a cached result when using Client Side Paging. Skip must be omitted or set to 0. You can use the cached copy of that first page, or you can re-execute the query to get a new result, discarding the previously cached result. Re-executing the query is useful when the data being fetched may change between two requests for the first page. Using the cached result is useful if you are paging back and forth through results that are not expected to change.
Valid Values:
When set to 0, the OData service caches the first page of results.
When set to 1, the OData service re-executes the query.
Default: 1
|
||||||||
|
Create Mapping
|
Determines whether the Rollbase table mapping files are to be (re)created.
The Hybrid Data Pipeline connectivity service automatically maps data store objects and fields to tables and columns the first time that it connects to the data store. The map includes both standard and custom objects and includes any relationships defined between objects.
Note: You must force creation of a new map when there is a change in the mapping options for the data source, or when the User Name / User ID connecting to the data source has changed. The mapping is tied to the user account that initially connects through the driver when the data source is created. If the user account is changed, then the map must be recreated. Simply change the value of the Create Map option to force creation of a new map.
|
||||||||
|
Map System Column Names
|
The mapSystemColumnNames parameter defines whether Hybrid Data Pipeline maps the integration name of standard columns that appear in each Rollbase object to a new name. By default, Hybrid Data Pipeline maps the id column to ROWID, and maps the remaining standard columns to a new name prefixed with SYS_ .
Valid values for mapSystemColumnNames are:
1 | 0
When set to 1, Hybrid Data Pipeline prefixes the names of standard columns of Rollbase objects with SYS_ or ROWID.
When set to 0, Hybrid Data Pipeline does not map the names of standard columns of Rollbase objects to new names.
Default: 1
|
||||||||
|
Uppercase Identifiers
|
Defines how Hybrid Data Pipeline maps identifiers. By default, all unquoted identifier names are mapped to uppercase. Identifiers are object names. Classes, methods, variables, interfaces, and database objects, such as tables, views, columns, indexes, triggers, procedures, constraints, and rules, can have identifiers.
Valid Values:
When set to ON, the connectivity service maps all identifier names to uppercase.
When set to OFF, Hybrid Data Pipeline maps identifiers to the mixed case name of the object being mapped. If mixed case identifiers are used, those identifiers must be quoted in SQL statements, and the case of the identifier, must exactly match the case of the identifier name.
Note: When object names are passed as arguments to catalog functions, the case of the value must match the case of the name in the database. If an unquoted identifier name was used when the object was created, the value passed to the catalog function must be uppercase because unquoted identifiers are converted to uppercase before being used. If a quoted identifier name was used when the object was created, the value passed to the catalog function must match the case of the name as it was defined. Object names in results returned from catalog functions are returned in the case that they are stored in the database.
For example, if Uppercase Identifiers is set to ON, to query the Account table you would need to specify:
SELECT "id", "name" FROM "Account"
Default: ON
|
||||||||
|
Use Integration Names
|
The useIntegrationNames map option is applicable only to data sources that access Rollbase data for either public cloud or private cloud (on-premise) applications. The useIntegrationNames parameter defines the type of name that Hybrid Data Pipeline uses for objects and fields. Every object in Rollbase has a singular name, a plural name, and an integration name. Every field in Rollbase has display name and an integration name. By default, when the map is generated, Hybrid Data Pipeline uses the singular name to generate the table names and the field's display name when generating the column names.
Hybrid Data Pipeline must use the integration names when communicating to Rollbase through the REST API.
To control the object and column names that Hybrid Data Pipeline uses when communicating to Rollbase, enable useIntegrationName in the Set Map Options section of the Mapping tab of your data source definition.
Valid Values:
0 | 1
If set to 1, Hybrid Data Pipeline uses the integration names to generate the table and column names.
If set to 0, Hybrid Data Pipeline uses the singular name to generate the table names and the field's display name when generating the column names when the map is generated.
The default value for useIntegrationNames is 0.
|
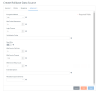
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
Encryption Method
|
Specifies whether SSL is used to communicate with the Rollbase Web Service. When SSL is enabled, the default, the driver uses the "https" scheme. When SSL is disabled, the driver uses the "http" scheme.
The default value is SSL.
|
|
Max Pooled Statements
|
The maximum number of prepared statements to cache for this connection. If the value of this property is set to 20, the connectivity service caches the last 20 prepared statements that are created by the application.
The default value of 0 means that the internal prepared statement pooling is not enabled.
|
|
Login Timeout
|
The amount of time, in seconds, to wait for a connection to be established before timing out the connection request.
When set to 0, the connection request never times out.
The default value is 0.
|
|
Initialization String
|
A semicolon delimited set of commands to be executed on the data store after Hybrid Data Pipeline has established and performed all initialization for the connection. If the execution of a SQL command fails, the connection attempt also fails and Hybrid Data Pipeline returns an error indicating which SQL commands failed.
Syntax:
command[[; command]...]
Where:
command
is a SQL command. Multiple commands must be separated by semicolons. In addition, if this property is specified in a connection URL, the entire value must be enclosed in parentheses when multiple commands are specified. For example, assuming a schema name of SFORCE:
InitializationString=(REFRESH SCHEMA SFORCE)
The default is an empty string.
|
|
Read Only
|
Sets the connection to read-only mode, that is, the data store can be read but not updated.
The default value is OFF.
|
|
Web Service Call Limit
|
The maximum number of Web service calls allowed to the cloud data store for a single SQL statement or metadata query.
|
|
Web Service Timeout
|
The maximum number of Web service calls allowed to the data store for a single SQL statement or metadata query. The value of 0 implies there is no limit.
The default value is 120.
|
|
Web Service Retry Count
|
Controls the number of times to retry a Select request that times out. call. Insert, Update, Delete requests are never retried. If set to 0, no retry attempts are made for Select requests that time out after the initial unsuccessful attempt. Valid values are from 0 and any positive integer.
The default value is 3.
|
|
Extended Options
|
Specifies a semi-colon delimited list of connection options and their values. Use this configuration option to set the value of undocumented connection options that are provided by Progress DataDirect technical support. You can include any valid connection option in the Extended Options string, for example:
Database=Server1;UndocumentedOption1=value[;UndocumentedOption2=value;]
If the Extended Options string contains option values that are also set in the setup dialog, the values of the options specified in the Extended Options string take precedence.
Valid Values: string
Default: empty string
|
|
Metadata Exposed Schemas
|
Restricts the metadata exposed by Hybrid Data Pipeline to a single schema. The metadata exposed in the SQL Editor, the Configure Schema Editor, and third party applications will be limited to the specified schema. JDBC, OData, and ODBC metadata calls will also be restricted. In addition, calls made with the Schema API will be limited to the specified schema.
Warning: This functionality should not be regarded as a security measure. While the Metadata Exposed Schemas option restricts the metadata exposed by Hybrid Data Pipeline to a single schema, it does not prevent queries against other schemas on the backend data store. As a matter of best practice, permissions should be set on the backend data store to control the ability of users to query data.
Valid Values
<schema>
Where:
<schema>
is the name of a valid schema on the backend data store.
Default: No schema is specified. Therefore, all schemas are exposed.
|