|
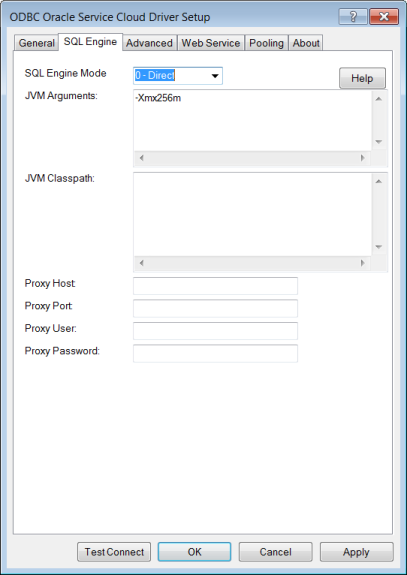
Connection Options: SQL Engine
|
Default (Direct Mode)
|
|
Specifies whether the driver’s SQL engine runs in the same process as the driver (direct mode) or runs in a process that is separate from the driver (server mode).
Default: 0 - Direct
|
|
|
A string that contains the arguments that are passed to the JVM that the driver is starting. The location of the JVM must be specified on the driver library path. Values that include special characters or spaces must be enclosed in curly braces { } when used in a connection string.
Default: -Xmx256m
|
|
|
Specifies the CLASSPATH for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) used by the driver. The CLASSPATH is the search string the JVM uses to locate the Java jar files the driver needs. Separate multiple jar files by a semi-colon on Windows platforms and by a colon on Linux and UNIX platforms. CLASSPATH values with multiple jar files must be enclosed in curly braces { } when used in a connection string.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the Hostname and possibly the Domain of the Proxy Server. The value specified can be a host name, a fully qualified domain name, or an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the port number where the Proxy Server is listening for HTTP and/or HTTPS requests.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the user name needed to connect to the Proxy Server.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the password needed to connect to the Proxy Server.
Default: None
|
|
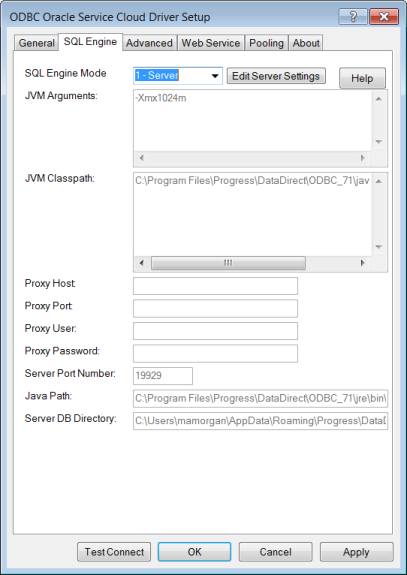
Configuration Options: SQL Engine Service
|
Description
|
|
Specifies whether the driver’s SQL engine runs in the same process as the driver (direct mode) or runs in a process that is separate from the driver (server mode).
Default: 1-Server
|
|
|
A string that contains the arguments that are passed to the JVM that the driver is starting. The location of the JVM must be specified on the driver library path. Values that include special characters or spaces must be enclosed in curly braces { } when used in a connection string.
Default: -Xmx1024m
|
|
|
Specifies the CLASSPATH for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) used by the driver. The CLASSPATH is the search string the JVM uses to locate the Java jar files the driver needs.
Separate multiple jar files by a semi-colon on Windows platforms and by a colon on Linux and UNIX platforms. CLASSPATH values with multiple jar files must be enclosed in curly braces { } when used in a connection string.
Default: install_dir\java\lib\rightnow.jar
|
|
|
Specifies the Hostname and possibly the Domain of the Proxy Server. The value specified can be a host name, a fully qualified domain name, or an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the port number where the Proxy Server is listening for HTTP and/or HTTPS requests.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the user name needed to connect to the Proxy Server.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies the password needed to connect to the Proxy Server.
Default: None
|
|
|
Specifies a valid port on which the SQL engine listens for requests from the driver.
Default: 19929
|
|
|
Specifies fully qualified path to the J2SE 5 or higher JVM executable that you want to use to run the SQL Engine Server. The path must not contain double quotation marks.
Default: install_dir\jre\bin\java.exe
|
|
|
Specifies the path of the working directory for the SQL engine service to use to store the newly created database files or locate the existing database files.
If the Database connection option contains a file name prefix, the user’s local database is created at the path specified by Server DB Directory. However, if the Database connection option contains a fully qualified path, the user’s local database is created using that path; the path specified by Server DB Directory is ignored.
Default: Path of the working directory for the SQL Engine service.
|