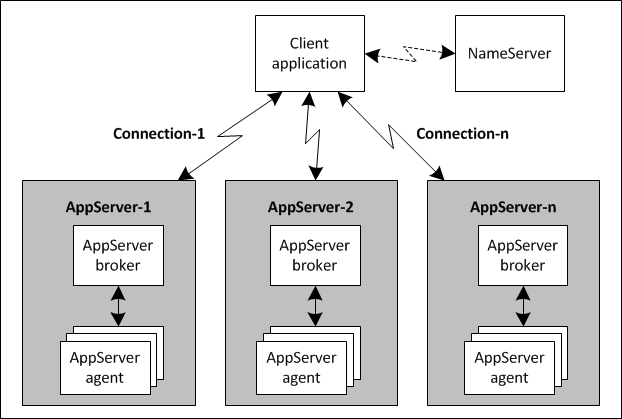
A client application physically connects to an AppServer with or without the help of a NameServer, as shown in the following figure.
The dotted arrows indicate optional communications required to establish a connection between a client application and AppServer instances using a NameServer. The NameServer is an optional component in the AppServer architecture. However, the NameServer is almost always used to support access to multiple AppServer instances that support a single application service. Otherwise, the client has to manage connections to each AppServer on its own, greatly increasing code complexity and connection management.
The NameServer maintains a list of the available AppServers in the network that provide a given application service. When the client application wants to connect to an AppServer, it requests an available AppServer from the NameServer and establishes the connection with the AppServer supplied. For more information on NameServers and how they coordinate AppServer connections for client applications, see the information on AppServer run-time components and operation in
OpenEdge Application Server: Administration. For more information on how AppServers maintain connections for client applications, see
Connection process.